Although tobacco companies now have the advantages of market control, policy protection and sufficient funds, they must be aware of the grim situation of foreign smoke and China, people's concern about tobacco hazards, enhance market awareness, adjust strategies in a timely manner, and optimize their own processes. Improve your own services, safeguard national interests, and meet the needs of consumers. Tobacco companies' sorting and distribution efficiency is a vital part of the company's operation process. To achieve efficient sorting and distribution, it is necessary to have efficient inbound and outbound capacity to match it. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the outflow process.
1 Radio Frequency Identification (RF1D) Technology
1.1 Overview of RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is an automatic identification technology that uses radio frequency signals and their spatial coupling and transmission characteristics for non-contact two-way communication to realize automatic identification of stationary or moving objects and data exchange. RFID has the advantages of long reading distance, fast reading speed, good readable and writability, simultaneous reading and writing of multiple items, and adapt to various working environments. With the continuous advancement of RFID technology, the cost is continuously reduced, and RFID begins to enter. Human logistics and supply chain areas.
1.2 RFID composition
The most basic RFID system consists of three parts: a tag, a reader, and an antenna, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 RFID system components
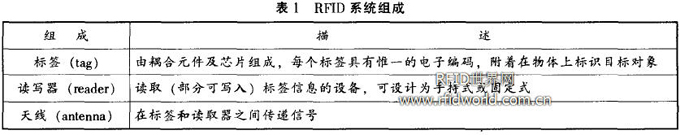
Composition description
A tag consists of a coupling element and a chip, each tag having a unique electronic code, attached to the object to identify the target object reader (reader) read (partially writable) tag information, can be designed to be handheld Or fixed antenna (antenna) transmits signals between the tag and the reader.
1, 3 working principle
In the practical application of RFID, the electronic tag is attached to the recognized object (surface or inside), when the identified item with the electronic tag passes within the readable range of the reader
(Figure 1).
The appointment identification information in the electronic tag is read out in a contactless manner, thereby realizing the function of automatically identifying the item or automatically collecting the item identification information.
1.4 Classification and working frequency

The method of obtaining energy by electronic tag can be generally classified into passive and active. The passive electronic tag itself does not have a power supply, and the voltage required for the operation is generated from the energy emitted by the reader through the antenna, which is characterized by light weight, small size, long life, but short working distance: the active electronic tag passes through itself. With battery power, it is characterized by long recognition distance, but high price and short life.
According to the type of memory of the electronic tag, it can be divided into two types: read-only and readable and writable. Generally, the size of the electronic tag memory can be from 16 bit to 512 Kbytes. Usually, the frequency used by the reader is called the 1-frequency of the RFID system, and can be divided into three ranges: low frequency (30 kHz to 300 kHz), high frequency (3 MHz to 30 MHz), and ultra high frequency (30 to 3 GHz). Common operating frequencies are low frequency 125KHz, high frequency l3.56MHz, and ultra high frequency 915MHz, 2, 54GHz. In general, an RFID system operating at frequencies below 100 MHz works by magnetic field coupling between coils. It usually has the characteristics of close working distance, low cost, large antenna size, and low communication speed: the RFID system above 40OMHz is It works by means of radio wave emission and reflection, and usually has the characteristics of long working distance, small antenna size and high communication speed. Different countries and regions have different regulations on frequency allocation and maximum transmit power.
With the maturity of electronic tag technology, the application of RFID technology is becoming more and more extensive. At present, Wal-Mart, the world's largest retailer, requires its top 300 suppliers to use electronic tags in 2007; China's second-generation ID card. Also based on the ISO/IEC14443-B standard 13.56MHz electronic tag, RFID technology is having a profound impact on our lives.
2 problem analysis
2.1 Characteristics of tobacco logistics
Tobacco logistics has its own characteristics relative to other logistics:
(1) Tobacco commercial enterprises implement the distribution mode of “sorting to distribution and delivery to householdsâ€. There are 4.4 million licensed cigarette retail customers nationwide, with a large number of retail customers, small orders, scattered varieties and frequent distribution: in terms of sales form Tobacco production enterprises mainly rely on the whole shipment, while tobacco circulation enterprises mainly rely on the delivery of goods.
(2) The unique shape and certain batch demand of the finished tobacco products form the demand for automatic processing.
(3) The speciality of the south of the sedge industry, smoking and health issues have been widely concerned by the society. The implementation of the Tobacco Control and Detective Convention by the Chinese government has been initiated, and the external environment for the development of the sloping industry will be subject to more stringent restrictions.
2.2 Analysis of the status quo of tobacco enterprises' warehousing
After the abolition of county-level legal person qualifications, 214 of the 348 prefecture-level cigarette commercial enterprises in the country have established their own logistics centers with different levels of sorting equipment, most of which are electronic label-assisted sorting lines. A very small number of companies have adopted sorting equipment with high automation and advanced configuration, such as Beijing, Shanghai, Dalian, Shenzhen, etc., but a large number of commercial enterprises also use manual sorting and outdated facilities.
The status of warehousing operations can be roughly divided into the following three categories:
The first category is fully automated, with industrial companies and some larger commercial companies.
The second type is semi-automatic operation. The storage is mainly on the shelf, and some forklift trucks are equipped with loading and unloading machinery, electronic label-assisted picking, and some are equipped with tower or vertical sorting machines. This type of method occupies a considerable proportion.
The third category is the human T operation, which is mainly based on flat storage, supplemented by tools such as forklifts. The storage areas are classified according to the ABC method and manually selected according to the characteristics of the tobacco enterprises. This type of development is shifting to semi-automated operations.
In the general prefecture-level tobacco companies, a variety of cigarettes are ordered an average of 80 to 110 times a day, and the top 20 or 30 varieties of the annual sales volume of 80%. On average, each order is ordered more than 400 times, and the largest variety is even ordered more than 1400 times. Such a high output frequency of a single variety, few other industries can have: In the face of the huge volume of modern cigarette sales, high-density warehousing frequency, manual warehousing or forklift trucks have become "incapable". This article is aimed at companies with annual sales below 300,000 boxes. Plan the design of the inbound and outbound process.
2.3 Process Design Principles
Tobacco business enterprise process design. It is necessary to implement a series of guidelines for the development of modern logistics by the State Tobacco Monopoly Administration. At the same time, we must consider the following points: to achieve system technology with advanced investment, practical and reliable, leaving room for upgrading: combined with existing facilities, it is necessary to prevent greed and seek for foreign affairs, and to prevent low-level redundant construction; Municipal companies of different scales, different markets, and different economic capabilities must seek truth from facts, scientific arguments, and treat them differently.
3 Solution design
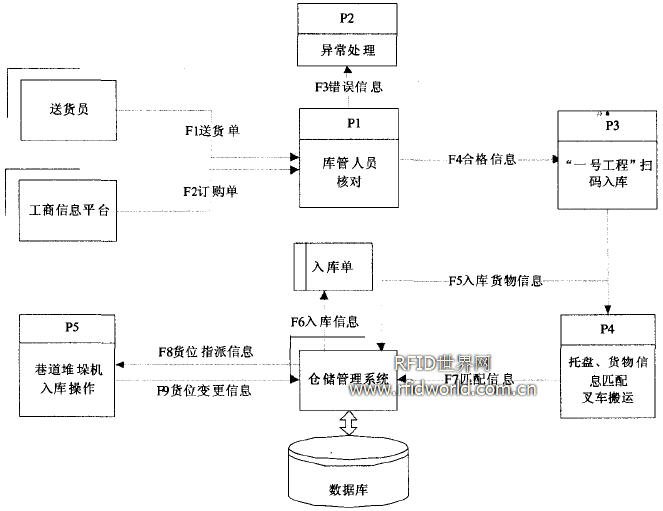
The semi-automatic way of storing tobacco commercial enterprises introduces certain automation technologies and machinery, supplemented by manual operations, to achieve a balance between efficiency and cost. Introduce the roadway stacker in the tobacco commercial enterprise towel, arrange the shelves reasonably, determine the number of roadways for the stacker service according to the frequency of the inbound and outbound and the stacking machine operation cycle, and then determine the number of stackers required to introduce the RFID system storage tray. , the shelf, the cargo turnover box to deploy electronic tags, corresponding to the forklift, roadway stacker, sorting terminal to deploy readers, and combined with tobacco "industry cigarette production and management decision management system project" (ie "No. 1 project", can Achieve “one dozen two sweepsâ€â€”the cigarette industry enterprise will paste the barcode issued by the competent department for each cigarette produced, and carry out the warehouse scan code and cigarette business enterprise warehousing scan code, so that the tobacco authorities can The provisions of the purchase, production, and sales information in a timely manner and effective control. The information collection is realized and connected with the warehouse management system. The data information is transmitted to the warehouse management system for storage, analysis and processing through the combination of wired and wireless, so as to achieve the purpose of rapid and transparent logistics control.
3.1 Data flow design
(1) Inbound data flow design (Figure 2).
(2) Outbound data flow design (Figure 3).
3.2 Business Process Design
In order to carry out effective positioning, the cargo space must first be encoded. The coded information is written to the shelf label, and the address code is generally used.
(1) Inbound business process design The delivery vehicle arrives at the storage station, and the warehouse management personnel first check the delivery note. After checking the correctness, the warehouse will scan the code through the “No. 1 Project†and collect the product information.
Passed to the warehouse management system to complete the handover of industrial and commercial goods. If the industry and commerce are transported by cigarettes, the same type of goods that have passed the “No. 1 Project†will be processed by the pallet. The forklift staff will use the readers on the forklift to scan the pallets with the pallets and the pallets. The barcode scanning of the product completes the matching of the tray information and the commodity information, and the matching information is wirelessly transmitted to the warehouse management system. The forklift truck delivers the goods to the roadway stacker or to the conveyor connected to it.
The warehouse management system determines the storage location of the commodity according to a preset storage strategy (such as classified random storage), the location assignment principle (such as first-in first-out), the commodity inventory status, etc., and transmits the allocated storage information to The on-site control system, the on-site control system drives the roadway stacker to complete the warehousing operation. The roadway stacker delivers the goods to the designated location. The RFID reader installed on the stacker scans the location information and transmits the information to the warehouse management system. The cargo information is updated and the storage operation is completed. If the pallets are transported between the industrial and commercial enterprises, the “No. 1 Project†in the storage stage can directly scan the pallet labels, and the matching product information can be obtained, and then the forklift is transported, and the roadway stacking machine is realized. The warehousing business process is shown in Figure 4.
(2) Outbound business process design
When there is a request for delivery. The warehouse management system determines the location of the goods to be delivered according to the inventory status and the outbound rules, and transmits the outbound information (such as the name, quantity, storage location, etc.) of the outbound goods to the on-site control system. The on-site control system drives the roadway stacker to operate to the designated location. The RFID reader automatically scans the location label for confirmation. After the completion of the update of the location information, the stacker sends the goods to the sorting system. The disk is removed and the tray is returned. The cigarette or the cigarette is sorted and scanned by the household, and the scan code information is transmitted to the warehouse management system to complete the inventory data update. After the sorting staff checks the sorted cigarettes correctly, the RFID reader is used to write the corresponding data to the turnover box label at the sorting terminal to prepare the loading and distribution. After the delivery is completed and the delivery is completed, the delivery personnel will return the tote to the warehouse, and the warehouse personnel will scan the tote label again. The label information is cleared for future use. The turnover box has the advantages of being rainable and reusable, being foldable, reducing the damage of the goods, and being environmentally friendly and pollution-free. Outbound business process is shown in Figure 5.
(3) After the introduction of RFID technology, the location information can be queried in real time to provide guidance for other operations. The query mainly includes the following two aspects:
1 Goods inquiry: the inventory quantity, distribution status of the goods, basic characteristics of the goods, etc.
2 Inquiring about the cargo space: the utilization of the cargo space (occupied cargo space, available cargo space, unavailable cargo space), cargo space utilization, etc.
4 Conclusion
The application of RFID technology to the warehousing process of the tobacco industry has not been implemented, and the following functions have been realized: the dynamic storage management of goods—using RFID technology, greatly improves the accuracy of collecting and collecting information records of goods entering and leaving the warehouse: Meeting customer needs— The roadway stacker is used to replace the forklift truck entering and leaving the warehouse and react quickly;
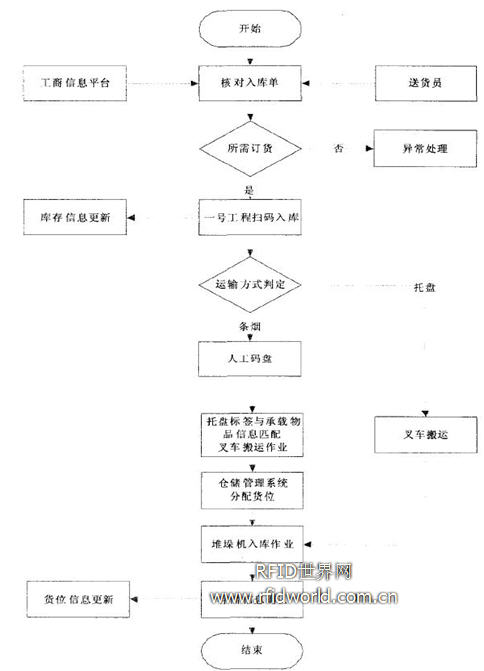
Figure 4 Warehousing business flow chart
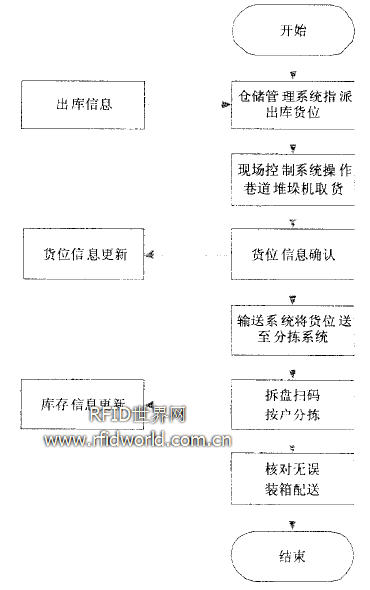
Figure 5 outbound business process
Increased warehouse utilization—package is compact and improves space utilization: a flexible and sustainable system—provides a good environment and interface for subsequent system upgrades: real-time warehouse monitoring—the system can display current inventory status and inventory levels in real time; The combination of wired/wireless technology for information transmission—real-time information collection and transmission can be effectively improved. Productivity: Simplified management – ​​reduced duplication of effort and reduced staff costs. This article only discusses an RFID-based solution for entering and leaving the warehouse. In actual management, it should be adjusted according to its actual situation. With the continuous improvement of the demand for automation technology in the tobacco industry, RFID technology will certainly have a broad application space.
steel plate for building, steel plate for roofing, galvanized roof steel
Henan Houming Industry Co., Ltd. , https://www.houmingsteel.com