In order to make scientific use of insect traps for forecasting or killing tea pests, and to provide scientific basis for the development and utilization of LED insecticidal lamps, the insect trapping test of lamp and the comparison test of different lamps were conducted. The test results show that the insect report lamp has a good trapping effect on tea pests, and preliminarily clarified termites, gold tortoises, leaf roller moths, tea silver ruler, tea scale insect, tung treeworm, tea spot moth, tea deer moth, tea white The annual fluctuations of the pests such as the striated scorpion, the black horned horned beetle, the tea longhorned beetle and the red-winged scorpion larvae were observed. The occurrence regularity and generation number of some pests were different from those recorded in the literature. The LED red insect light has no trapping effect on insects, and the blue insecticidal lamp has a stronger insect trapping ability than the violet insecticidal lamp. Among them, the violet insecticidal lamp has a greater ability to trap Lepidoptera than the blue insect lamp, and traps the tea tree sheath wings The ability of insect pests and natural enemies is also stronger than that of the blue-light insecticidal lamp. The ability of the blue-light insect lamp to attract Hemipteran, Diptera, Homoptera, and Moth insects is stronger than that of the violet insect killer lamp. The ability to attract concentrated insects (mosquitoes and cockroaches) is worse than that of the blue light insecticidal lamps. The ability to trap tea pests and natural enemies is much better than that of the violet light insect killer and the blue light insect killer, especially for natural enemies. force. In addition, the spectrum of the trapping lamp is wider than the violet insect killer and the blue light insect killer. The frequency-vibration trap lamp is suitable for tea plant pest monitoring, or trapping and killing insect pests at the peak of adult crops. The LED insecticidal lamp has the prospect of development and utilization.
0 INTRODUCTION Frequency vibration type insecticidal lamp is a new type of plant protection lamp developed in recent years. It has the sensory advantages of attracting insect species and quantity, and high insecticidal efficiency. It attracts insect species and ordinary black light (or incandescent lamp). Lamps) The same or slightly more, trapping a variety of insects is significantly more than the ordinary black light (or incandescent lamp), the efficiency of the 30 W frequency vibration type insecticidal lamp applied to kill the woodland American white moth than 1000 W trapping electric shock The moth lamp and the 250 W insect trap are good. The Jiaduo automatic insect report lamp is in line with the normal black light or incandescent lamp to monitor the growth and decay of the pest. The adult, early and peak periods of the adult under the lamp are earlier, and the adult peak is more High, reflecting the change is more pronounced and accurate, and it is a better pest monitoring tool. Jiaduo Frequency Trembler Grid Lamps are widely used for the prevention and control of farmland pests, and have achieved good results. The application results of tea gardens also give positive recognition to this light, but the light's selectivity is not strong, and it is natural enemies and other harmless insects. Also has a strong ability to kill. At present, in addition to reports on the law of the annual growth and decline of tea pest insects, little is known about the tea moth [15].
LED is the fourth generation of semiconductor lighting materials, its narrow spectrum, pure light, and more conducive to the use of specific spectrum to accurately lock target pests, to avoid indiscriminate killing, to maximize the use of ecological control functions. Moreover, the lamp has the advantages of low power consumption, long life, etc., and will be widely used in the field of ecological regulation of pests. However, there have been no reports of LED trapping of tea plant insects.
In order to make scientific use of insect traps to predict or trap and kill tea pests, the author conducted a systematic survey of trapping effects of frequency vibration traps on tea plant pests in 2007-2008, and carried out frequency-vibration insecticidal lamps. LED insect pests with different frequencies of the light source were used to trap the insects in the tea plant. The results are reported below.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Test lamps LED insecticidal lamp, divided into violet, red and blue light three kinds of bands, effective peaks were 385 ~ 390 nm, 660 nm and 450 nm, power is 7 W, Xiamen Jing Ji Le Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. developed and produced ; Jiaduo vibration type insecticidal lamp, PS-15II/H (light control), effective peak 320 ~ 400 nm. Power is 30 W, Jiadoko Electronics Industry and Trade Co., Ltd. production; Jiaduo brand insect reporting lamp, JDA type, 20 W black light tube, Jia Duoke Industry and Trade Co., Ltd. production.
1.2 Test methods The lamps and lanterns refer to the instruction manual for installation. In 2007, in the Tea Research Institute of the Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Pingyuan District, a tea light trapping test was conducted on Jiaduo Insect Test Reports. In 2008, a comparative test on different light source pest killing lamps was conducted in the same tea plantation. The tea plantation in the tea plantation is 0.80 m high, in which the frequency-vibration insect killer, LED violet and blue light insect killer lamps are arranged in triangles. The distance between the lamps is 38 m and the height is 1.8 m. The light control is turned on at the same time every night. The next day inspection Count the insects trapped by each lamp.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Insect Trachea Insect Trachea Insect Traps In March-December 2007, 253 days were actually turned on during the entire experimental period, and a total of 15,354 insect pests were trapped in various tea gardens, including Lepidoptera Use californium, tung tree ulnar, tea silver ruler, tea spot moth, tea deer moth, tea roll leaf moth, tea leaf roller moth, tea moth, tea moth moth, tea moth moth, tea leopard moth, tea white tussock moth, double line There were a total of 3,175 larvae, moths, Spodoptera littoralis, Scrophulariella moth, Spodoptera littoralis, Spodoptera moth, Tetranychus urticae, and tea tree hawk moth, etc.); Coleoptera (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Cerambycidae, There were a total of 7988 heads of Red-winged longhorn beetles, tea-star longhorn beetles, etc.; 296 heads of Orthoptera (African apes, brown cockroaches, big cockroaches, etc.); 3875 heads of Isoptera heads, and 20 heads of Homoptera. In addition, a large number of small green leafhoppers on the lamp tube were observed under the lamp, but very few leafhoppers were found in the insect bag under the lamp, which may be related to the density of the high voltage power grid of the lamp. No phototaxis was observed in the important pests of tea in Lidong tea region, such as Lizard's Weevil, Black Stork's beetle, and Tea Grey's weevil.
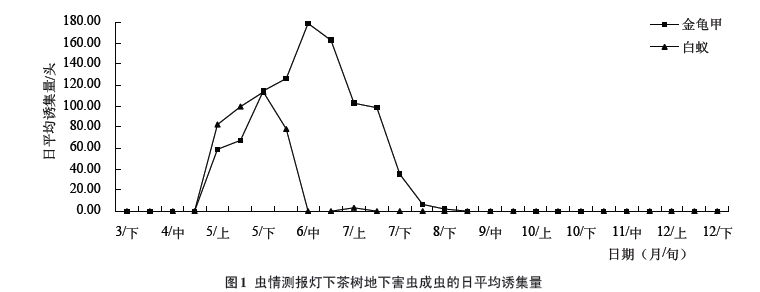
2.2 The main pests in tea plantations and their annual growth and decline
2.2.1 Tendency of tea pests under the light of pests under soil lamp The trapping test of insect pests on the tea tree shows that the termite adults first appeared in early May and finally appeared in the middle of July, from early May to early June. For the peak period of this insect pest, the average daily trapping amount was 78-114 heads per day. The insects are clustered and relatively concentrated in insects. The actual number of insects is 13 days, an average of 298 heads per day, and a maximum of 1,000 heads per day. The first year of the worm year occurred. Most observations under the lamp appeared after a sweltering rainstorm. The golden tortoiseshell was first seen in late April and finally seen in late August. From early May to early June it was the peak of the insect's infestation. The average number of traps reached 35 to 178 head days, and the maximum trap was over 400 heads/day.
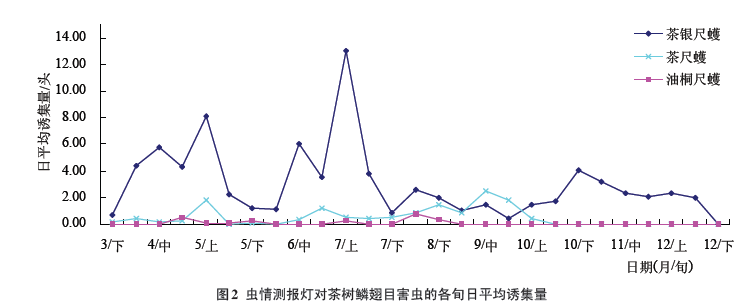
2.2.2 Phytophthora infestans under the light of tea Lepidoptera The changes in trapping amount under the light of the insect pests in the tea garden, Lepidoptera moth (Fig. 2) show that all the insect stages are visible throughout the year, except for the early April-early April. In addition, mid-June to mid-July, there was a peak of moth traps. At other times, the amount of moth trapped was relatively stable and there were no generational boundaries. The Oxyridis adult can be found in late March and finally seen in early October. Adults are trapped from late March to early May, late May and mid-June to early October, indicating that there are overlapping generations and annual occurrences. More than 4 generations old; T. cinquefoliensis trapped adults in late April, late May, early July, and late August, and the time is relatively concentrated, indicating that the worms occur annually in the tea region. generation. The occurrence of the above three pests is consistent with the actual situation in the tea garden.
The annual changes in the trapping volume of tea spot moths, tea deer moths, and tea-white moths (Figure 3) indicate that the tea spot moths are in mid-April, late-March, mid-August, and late September to October In the late days of trapping into adults, the worm's generation time should be more than 38 days [18]. According to the initial judgment period of the moth time period and generational time, 4 generations may occur, which is more than the previously recorded algebra (ie April, July, October) More than one generation [19], whether it is related to the progress of feathering or climate change in recent years, remains to be confirmed. The tea deer moths were found to be adult in mid-April, early May, mid-June, late July and early September to mid-December respectively. Among them, there was a peak from early October to early November, according to the adults under the lamp. The actual time interval that emerged preliminarily determines that the occurrence of the tea area should be no less than 3 generations. There are two obvious moth-eating time periods throughout the year, from April 1 to May 7 and July 16 to October 21, and the previous record (ie, the adult's peak period is April, June, August and October [19] could not fully correspond and needs further confirmation.
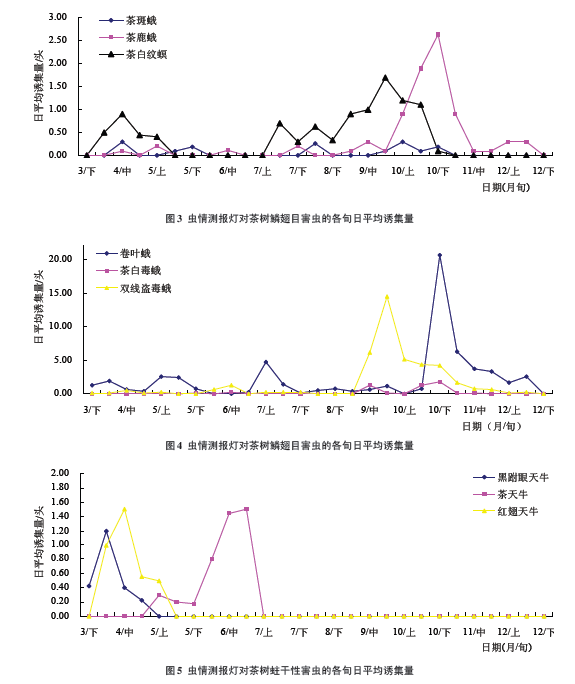
The annual trend of trapping amounts of the two-line larvae, the white tussock moth, and the moth-like pests (Fig. 4) shows that the double-line larvae are seen on March 29, last on December 16 and early April. Adults can be trapped from early May, late May to mid-June, early July to late July and mid-September to early December, with the largest amount of trapping from mid-September to late October. For the peak period of the moth outbreak, the initial judgment of the occurrence of the year should be more than 4 generations, or related to the existence of a different host. The tea white poisonous moth sees on the first day of May 28 and lasts on November 16th, that is, in late May, mid-June, late September, mid-October and mid-November, the preliminary judgment of the occurrence of the larvae is 3 The ~4 generation, far less than 7 generations [19], may be related to the amount of occurrence that affects the amount of trapping. The dominant species of tussock moth pests in Qidong tea region are tea leaf roller moth and tea roller leaf roller moth, both of which occur 6 generations in a year, and the generations are severely overlapped. The time of occurrence is similar to that of habit, and the mixture often occurs. Trapping statistics showed that the pests had a small peak in early April, early May, and early July, peaking gradually, reaching the highest peak of the year until late October, and then decreasing until mid-December. There are more wormholes.
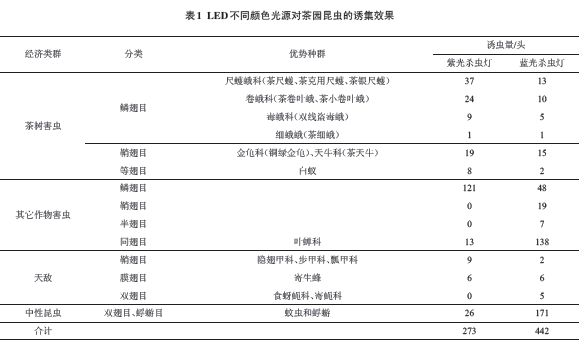
2.2.3 Regularity of Decrease under the Dry Insect Pests of Tea Plants In the East of the Chadong Area, there are black-sucking day-long-horned beetles, tea long-horned beetles, and red-winged long-horned beetles, which occur one generation each year. The results of the lamp trapping test showed that (Figure 5) the adults of the Black-sucked Skylark appeared from late March to mid-April, and finally found on April 27; the tea-herd-tailed cow was found on May 9 and was finally seen on July 7. In June, the red-winged longhorn beet was seen on April 4 and finally appeared on May 8, from early April to early May. Among them, the black-white-eyed longhorned beetle and the longhorned longhorned beetle were earlier and delayed by about 30 days than the records of this time [19].
2.3 Comparison of the trapping and killing effects of different light source insecticide lamps on tea plant pests
2.3.1 Comparison of Red, Violet and Blue Lights of LEDs The tests were conducted between March and June 2008. The results showed that no insects were trapped in the red insecticidal lamp during the experiment, and the red light may not induce insects. Set role. The statistical results of the 23-day trapping data for the purple insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp showed that (Table 1) the total number of insect traps for the blue insecticidal lamp was 442 heads, which was 1.6 times that of the violet insect killer lamp; the purple insect killer lamp The total amount of lepidopteran insects and tea tree moth pests collected was 192 and 71 insects, respectively 2.5 times and 2.5 times that of the blue light insecticidal lamp. Among them, the violet insecticidal lamp was used to trap the Polygonidae and Toxoplasma. The number of tea pests of the genus Moth is 2.6 times, 2.4 times, and 1.8 times that of the Blu-ray insecticidal lamp, respectively, indicating that the violet insect lamp has stronger moth trapping ability and is more suitable for trapping and killing Lepidoptera pests than blue light insect lamps; The total amount of tea tree coleopteran pests and tea garden coleoptera natural enemies collected by insecticidal lamp were 19 and 9 respectively, which were 1.3 times and 4.5 times respectively, indicating that blue light insect traps trap tea tree coleopteran pests. And the natural enemies are more capable, but the ratio of harm to damage of Coleoptera insects induced by the violet insecticidal lamp is 1:2.1, while that of the blue light insecticidal lamp is 1:7.5. Therefore, relative to the tea garden attracting Coleoptera pests, the blue light insecticidal lamp has a good comprehensive effect, and the use of the purple light insecticidal lamp may be more likely to kill natural enemies of Coleoptera; blue light insecticidal lamp traps other crops leafhoppers as an advantage The number of species of homopteran pests is 138, which is 10.6 times that of the violet insecticidal lamp, indicating that the blue light insect lamp can effectively control the damage of leafhoppers; the blue light insect lamp attracts mosquitoes and cockroaches of tea garden neutral insects. It is 171 heads, which is 6.6 times that of the purple insect killer lamp, which shows that the blue light insect killer has a greater lethality to neutral insects than the violet light insect killer; in addition, the violet insect light has a strong ability to trap termites, and the blue light kills Insect bugs are more capable of trapping bugs. It can be seen that the purple insecticidal lamp has strong ability to attract moths, and the blue insecticidal lamp has strong ability to induce adult insects of leafhoppers, and the blue light insecticidal lamp can kill a large number of neutral insects, and the purple insect lamp has greater potential harm to beneficial beetles; The insect trapping spectrum of the violet insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp are different.
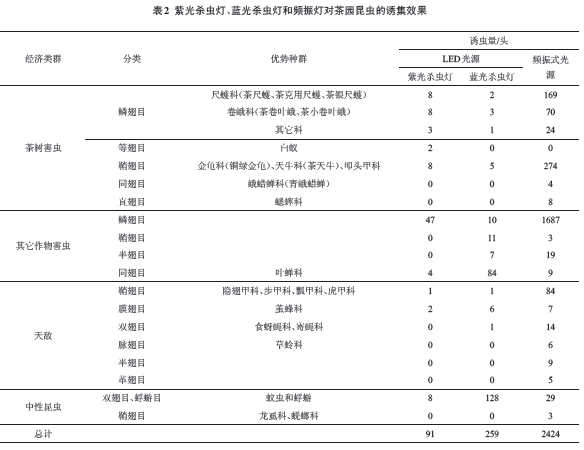
2.3.2 Comparison between LED and frequency-oscillation type The statistical results of 15 days of trapping data for the violet insecticidal lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp indicate (Table 2) the differences in the insect trapping amount between the violet insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp. The difference was basically the same as that of the 23-day trapping amount, except that the number of samples was small, and the difference range was changed. The number of trapped insect pests of the Jiaduo Frequency Trembler Grid Lamp was 2424 for 15 days, which was 26.6 and 9.4 times that of the violet insecticidal lamp and the blue light insecticidal lamp, respectively. The amount of trapped insects for the Lepidoptera was 1950 heads, which were Vicious and blue light insect killer lamps were 29.6 and 121.9 times higher, and the trapping amounts of tea tree moth pests were 7.6 times and 43.8 times higher than those of the violet insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp, respectively, and the trapping amount of Coleoptera insects was It was 364 heads, which were 40.4 times and 21.4 times respectively of the purple insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp. Among them, the trapping amount of the tea tree coleopteran insect pests was 34.3 times and 54.8 times respectively for the purple insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp. The trapping amount of Coleoptera natural enemies is 84 times that of the violet insect killer lamp and the blue light insect killer lamp. The ratio of the benefit of the frequency oscillator lamp, the violet insect killer lamp and the blue light insect lamp to the tea tree Coleoptera insects (tea tree Coleoptera insect pest: coleoptera (natural enemies) are 1:5.7, 1:8, and 1:5, respectively, and the benefits are only slightly better than the blue-light insecticidal lamp; the trapping amount of the Homoptera insects is only 13 heads, which is more than that of the purple insect lamp, but only 10.71% of the blue light insecticidal lamp, the trapping effect is not good; the trapping amount of neutral insects such as mosquitoes and cockroaches is only 29, compared with the purple light Insect lamps are many, only 22.66% of the blue light insect killer lamp, avoiding a large number of killing neutral insects, are conducive to the protection of biodiversity; Jiaduo frequency-vibrancy insecticidal lamp, purple insecticidal lamp and blue light insect lamp to attract tea pests The ratio of hazards to natural enemies was 1:4.4, 1:9.7, and 1:1.4, respectively, and the trapping efficiency was better than that of the blue light insect killer. In addition, the Jiaduo Frequency Trembler Grid Lamps also attracted lusterless insects and blue light insect traps that were not trapped during the experiment. Insects, especially those that kill and kill natural enemies of the order Hemiptera, Cyprinidae, and Dermaoptera, deserve attention in their use. It can be seen that the frequency-vibrating lamp has a great killing effect on insects, and its insect trapping spectrum is wider than that of a violet light and a blue light insect killer lamp, but whether it is the same as a violet light insect killer lamp and a blue light insect killer lamp and a lot of frequency vibration type The difference in insecticidal light intensity is relevant and needs further study.
3 Discussion (1) Jiaduo Insect Report Lamp has a wide spectral range, large insect attracting spectrum, and large insect trapping efficiency. However, large numbers of tea garden natural enemies or non-target insects were observed under the lamp. Therefore, according to the occurrence of major local pests, scientific lighting regulations should be formulated to avoid long-term lighting.
(2) There are differences between some tea pest pests and the records of occurrence and generation of records in the pest control report lamp. It may take many years to correct the results, and some pests occur in relatively small amounts, peaks are not obvious. Accuracy. At the same time, changes in climate, agronomic practices, and species structure will also affect the occurrence of pests, pending further study.
(3) Jiaduo Frequency Trembler Grid Lamps have been widely used in tea gardens, especially organic tea bases. However, the amount of traps for non-target insects is large and there may be potential hazards to biodiversity. They should be used in mountain forests. .
(4) The LED insecticidal lamp has a narrow spectral range and good selectivity, and is suitable for trapping and killing tea plant pests. If we can design a simple replaceable light source combined with adjustable gap insecticidal grid can give full play to its advantages and promote its use in the tea area.
Related Products: Artificial Climate Room Portable Agricultural Environment Monitor
Tipper trailers,Dump Trailers,Dumping Tipper Semi Trailer
Shandong Tenda Vehicle Co. LTD , https://www.tendavehicle.com